Generative AI is revolutionizing the way businesses operate by automating and systematizing tasks that once required extensive human effort. Much like how spreadsheet software transformed financial modeling, generative AI is set to make specialized skills more accessible through prompt engineering. This technology not only speeds up operations but also enhances decision-making by analyzing large datasets, thereby augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them.
Generative AI can accelerate and imporve the quality of the outputsof business processes in two key ways:
- Streamlining Operations - Generative AI can handle complex end-to-end tasks like generating marketing copy, summarizing clinical trials, and drafting contracts without any human involvement, enabling workers to focus on higher-value responsibilities.
- Enhance Decision Making - generative AI enhances the speed and quality of business decision-making. These models can rapidly analyze massive datasets, identifying patterns that even the most skilled analysts would likely overlook. This allows employees narrow their focus and energies on the most essential aspects of problem solving creativity.
Streamlining Operations
One of the most immediate benefits of generative AI is its ability to dramatically accelerate business processes. Technologies like natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and robotic process automation (RPA) have already had an impact. But generative models take it to the next level by handling complex multipart tasks end-to-end without human involvement.
For example, generative AI can generate unique marketing copy tailored to specific campaigns and audiences. It can synthesize data from clinical trials into easily digestible reports for regulators. Generative models can even draft legal contracts, impersonating the writing style of veteran lawyers in a fraction of the time.
Imagine a customer service department where chatbots handle routine queries, freeing up human agents to tackle more complex issues. Or consider a supply chain where AI algorithms optimize logistics, reducing both time and costs.
The key point here is that generative AI takes over tasks that are time-consuming but not necessarily complex, allowing human workers to focus on areas that require creativity or nuanced understanding.
Enhancing Decision-Making
In addition to efficiency gains, generative AI enhances the speed and quality of business decision-making. Businesses are often swamped with data, and sifting through it manually to identify useful insights can be a herculean task.
These models can rapidly analyze massive datasets, identifying patterns that even the most skilled analysts would likely overlook.
For instance, AI algorithms can analyze consumer behavior to help retailers make informed decisions about inventory management. The result is quicker, more accurate decision-making that can give businesses a competitive edge.
Marketers can tap generative AI to predict consumer behavior and adjust product offerings accordingly. For example, algorithms can forecast which items are likely to sell out or flop. Supply chain managers can leverage AI-optimized logistics to minimize costs and delivery times. Generative models can also synthesize insights from clinical studies to accelerate drug development.
The key is combining the strengths of human intuition and AI-powered analytics. With the right integration, companies can make optimal data-driven decisions with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
The Spreadsheet Revolution
Can you imagine life without spreadsheets?
To understand the potential of generative AI, it's useful to look back at the transformative effect of spreadsheet software on businesses. Before spreadsheets, financial modeling was a labor-intensive process that required teams of accountants. Spreadsheet software automated many of these tasks, allowing a single analyst to do the work that previously required a team. The software didn't make accountants obsolete; instead, it made them more valuable by freeing them to focus on more strategic tasks.
The Generative Advantage
Generative AI aims to do for specialized tasks what spreadsheets did for financial modeling. Where analysts once constructed financial models manually, now anyone can do so at the click of a button.
Whether it's drafting legal contracts or summarizing clinical trial data, these tasks often require specialized knowledge and are time-consuming.
Generative AI can handle these tasks efficiently, turning specialized skill sets into something more generalizable. Just as you don't need to be a math whiz to use a spreadsheet, you won't need to be a legal expert to draft a basic contract if you have access to advanced AI tools.
Similarly, generative models collapse specialized skill sets into prompt engineering, augmenting human capabilities.
Companies that leverage these technologies will accelerate product development, improve decision quality, and maximize efficiency. Those that neglect generative AI risk obsolescence. The competitive advantages are too significant to ignore. But integration must be strategic and thoughtful. If done right, generative AI can unlock unprecedented value, innovation, and growth.
Business leaders must ask themselves:
Will you lead the transition to an AI-enabled enterprise, or will you allow competitors to disrupt your organization?
Are you prepared to integrate these advanced AI tools into your business model, and if not, are you willing to risk falling behind those who do?
The generative AI train is leaving the station. Climb aboard now, or risk being left behind.
Deploying Generative AI Starts Here
The potential of generative AI is clear. But how can companies actually integrate these powerful models into their operations? Successfully deploying generative AI requires three key elements:
- Strategic Process
- Tailored Technology
- Enabling Roles
We've addressed these in several key articles we recommend for you review.
1 Strategic Process
First, organizations need a thoughtful process and plan for deploying AI. Which business processes should be augmented first? How will workflows need to adapt? What risks or challenges may arise? By proactively addressing these questions, companies can ensure a smooth and effective integration.
The process should involve stakeholders at all levels to assess needs, surface concerns, and gain buy-in. Ongoing iteration and testing is also crucial to refine the AI deployment over time.

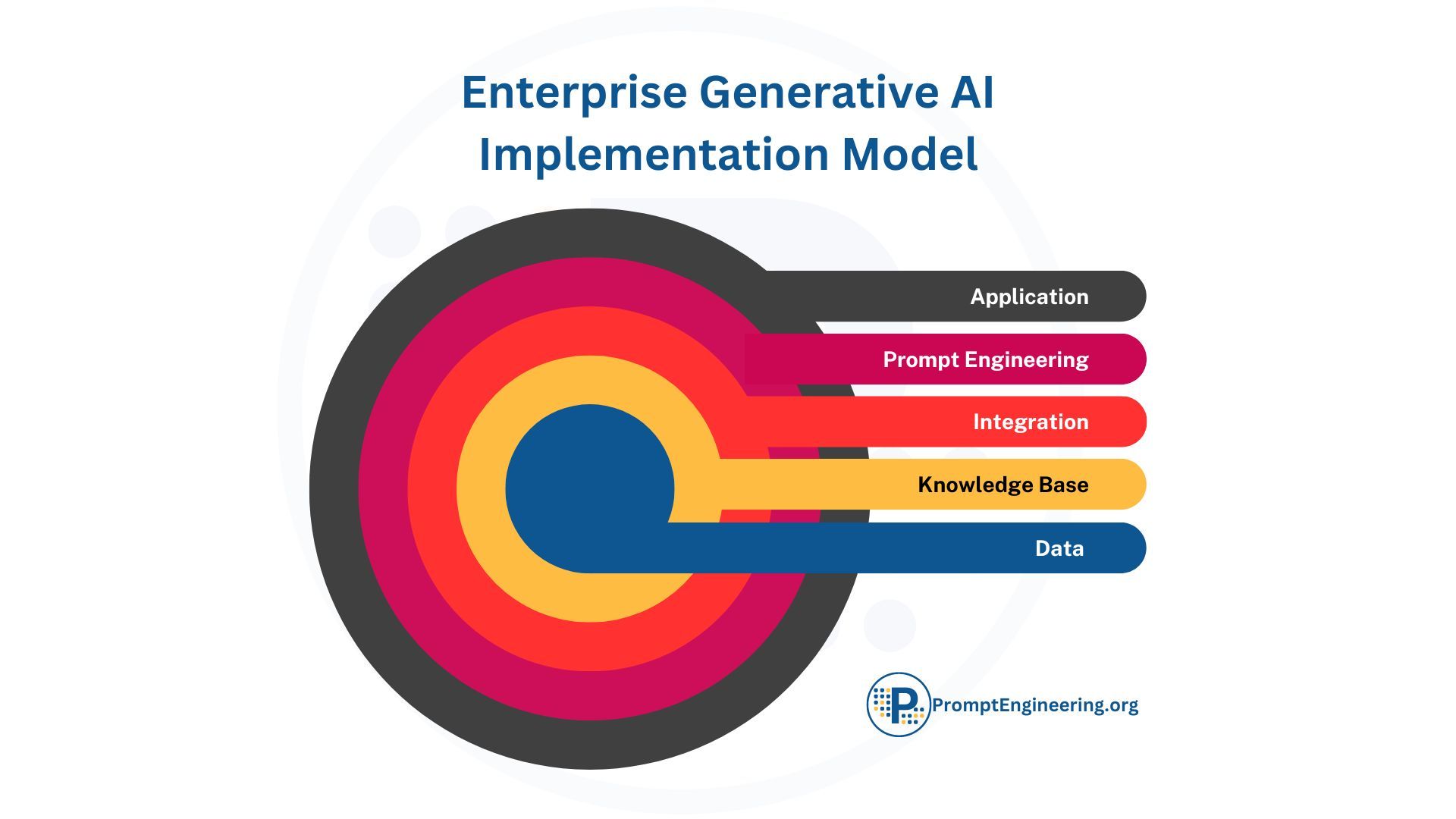
2 Tailored Technology
Next, companies must select the right AI technology for their specific use cases. The space is evolving rapidly. There are cutting-edge models like GPT-3 and DALL-E along with more specialized tools for distinct tasks. Organizations should fully evaluate their options to determine the best tech for their needs.
Key criteria include accuracy, efficiency gains, ease of integration, and total cost of ownership. Assessing tradeoffs around build vs buy decisions will help strike the optimal balance.
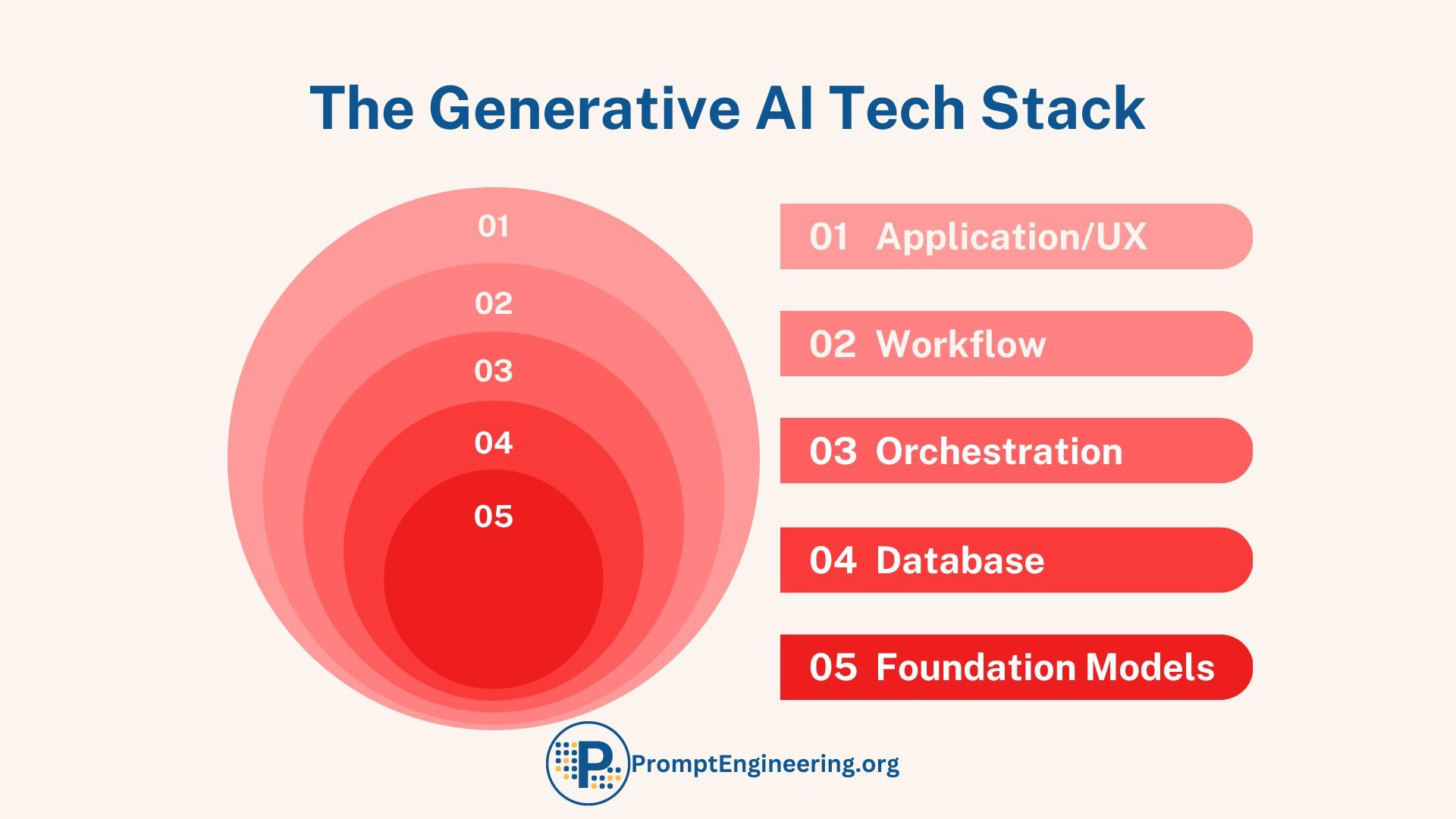
Enabling Roles
Finally, companies need the right mix of human roles and responsibilities to enable generative AI. A new capability like "prompt engineering" is required to translate business problems into effective AI prompts. Domain experts ensure output quality. IT specialists can handle technical integration.
Dedicated roles to monitor model performance, suggest improvements, and communicate impact are also important. As technology evolves, so must the surrounding organizational structures and skill sets.