Introducing Dr GPT? One might be tempted to think so after perusing a recent paper entitled, "Exploring GPT-4's Potential in Medical Challenge Problems," published on March 24th.
This fascinating study delves into the performance of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 on medical competency exams, with a focus on simplicity and benchmarking against other models, such as Flan-PaLM 540B. The enlightening results offer valuable insights into the potential applications of GPT-4 and AI within the healthcare and medical sectors. In this discussion, we will examine the outcomes, discoveries, and broader implications of GPT-4 and AI in the realm of medicine.

GPT-4's Impressive Performance in Medical Exams
On the USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Examination) Self Assessment and Sample Exam, GPT-4 achieved an overall average score of 86.65% (5-shot) and 83.76% (zero-shot), compared to GPT-3.5's 53.61% (5-shot) and 49.10% (zero-shot). GPT-4's performance remained impressive on questions referencing visual media, even though the media elements were not passed to the model.
On the multiple-choice components of MultiMedQA, GPT-4 outperformed GPT-3.5 and Flan-PaLM 540B on every dataset except PubMedQA (slightly outperformed by Flan-PaLM 540B). It also demonstrated strong performance on non-English language questions.
Surpassing the USMLE Passing Threshold
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) has a passing threshold that requires examinees to answer approximately 60% of multiple-choice questions correctly. While GPT-3.5 was approaching this threshold, GPT-4 surpasses it by a considerable margin. For medical professionals, this signifies that GPT-4 could be a valuable study tool in preparing for these critical exams.
Overcoming Language- and Vision-Centric Challenges
It is particularly impressive that GPT-4 performs well on USMLE Self-Assessment and Sample Exam questions, even without the ability to process visual media elements like graphs, photographs, and charts. Despite not receiving media information, GPT-4 still managed to achieve 70-80% prediction accuracies on questions containing media elements. This showcases the model's adaptability and robustness in understanding context, even without all the necessary information.
The study stated “Investigating these phenomena further revealed that, despite not being able to see relevant images, the text-only GPT-4 model is often able to employ logical reasoning and test-taking strategies to select a reasonable answer choice"
By further developing GPT-4's capabilities to process visual media, it could become an even more powerful tool for medical practitioners and researchers.

GPT-4's Reasoning Capabilities
The sample output provided by the study showcased GPT-4's ability to reason about complex medical concepts tested in USMLE challenge problems. These include an explanation, counterfactual reasoning, differential diagnosis, and testing strategies. For example, GPT-4 can help medical professionals narrow down possible diagnoses based on a patient's symptoms and suggest relevant tests to confirm the diagnosis.


Understanding Errors and Hypothesizing Mistakes
One of the most impressive aspects of GPT-4 is its ability to understand and analyze a student's errors. When a student makes a mistake, GPT-4 can hypothesize why the error occurred and provide guidance on how to avoid similar errors in the future. This personalized feedback can be invaluable in helping students grasp difficult concepts and improve their overall understanding of the subject matter.


Conducting Counterfactual Analysis
GPT-4 goes beyond simple explanations by conducting counterfactual analyses. This means the model can create alternative scenarios or variations of a given problem, allowing students to explore different possibilities and understand the consequences of their decisions. This type of learning can help students build critical thinking and problem-solving skills, essential for professionals in the medical field.
Performance Across Different Languages and Regions
The MedQA dataset includes examination questions from mainland China, Taiwan, and the United States, covering English, simplified Chinese, and traditional Chinese. GPT-4 performs well on difficult questions presented in non-English languages, scoring over 70%, indicating its potential for multilingual medical applications. Medical professionals and researchers in various regions could benefit from GPT-4's ability to understand and process information in multiple languages.
Importance of Calibration in High-Stakes Domains
Calibration is a key factor when it comes to language models like GPT-4. It measures how well the model's predicted probabilities align with the actual outcomes. In fields like medicine, calibration is crucial because it impacts the trustworthiness and interpretability of the model's output. For example, accurate probability estimates for treatment success can help doctors weigh the risks and benefits of a therapy plan. As language models become more prominent in high-stakes areas, well-calibrated models will play a critical role in decision-making processes.
Comparing GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 Calibration
When comparing the calibration of GPT-4 to its predecessor, GPT-3.5, using official USMLE datasets, GPT-4 demonstrates significantly better calibration. For instance, when GPT-4 assigns an average probability of 0.96, the answer is correct 93% of the time. In contrast, GPT-3.5's answers with similar probabilities are only correct 55% of the time. As indicated, this improvement in calibration is essential for applications in medicine and other high-stakes fields, as it increases the trustworthiness of the model's output.
Real-Life Implications for Professionals
Ultimately, improved calibration in models like GPT-4 can lead to better patient outcomes and more effective treatments. For the wider business community, a well-calibrated model can be invaluable for decision-making in high-stakes situations, such as investment strategies, risk assessments, and supply chain management. The enhanced reliability and interpretability of these models can help professionals make more informed decisions, minimizing potential risks and maximizing opportunities.
The Need For Prompt Engineering: Exploring Richer Prompting Strategies
GPT-4 has shown great potential in answering USMLE multiple-choice questions. However, there's room for improvement by exploring richer promoting strategies. Methods like a chain of thought prompting, self-consistency prompting, and providing models with information retrieval tools have proven to enhance performance in the past. As GPT-4 is a new model, finding the optimal prompting pattern could lead to even better results.
Chain of Thought Prompting: A Two-Stage Approach
Chain of thought prompting is a two-stage approach where the model first lays out its reasoning step by step and then provides a final prediction based on that reasoning. Although this technique hasn't shown significant performance improvements on medical questions for GPT-4, it's possible that a different prompt structure could be more effective in the future.
Picture a scenario where a medical professional asks GPT-4 to identify the most suitable treatment for a patient. By using a chain of thought prompting, the AI would first consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and potential complications before recommending the best course of action.
Few-Shot Example Curation: Expert Input vs Random Selection
Few-shot example curation involves using a panel of experts to select the best demonstration examples for few-shot prompts. A study compared the performance of GPT-4 using expert-curated examples with a random selection strategy, and the results were similar across different datasets. This suggests that expert curation might not be necessary for achieving strong performance with the latest generation of language models like GPT-4.
Imagine a hospital using GPT-4 to streamline patient care. Whether the AI is trained with expert-curated examples or random selections, the outcomes would be comparable, potentially saving time and resources in the training process.
Memorization Concerns in GPT-4
The impressive performance of GPT-4 on benchmark datasets raises concerns about whether it relies on memorization or leakage effects. Leakage can occur if the model's training set includes benchmark data. Since large language models like GPT-4 are trained on massive datasets from the internet, it's possible that benchmark data might accidentally end up in the training set.
To probe for memorization, the researchers developed a heuristic algorithm called Memorization Effects Levenshtein Detector (MELD). MELD helps identify potential signs of leakage by evaluating the model in a black-box manner. The algorithm prompts the model to generate a long set of near-exact matches to a given data sample and then assesses the similarity between the generated data and the initial data. If MELD detects a potential match, it's likely that the data was part of the model's training set and has been memorized.
When MELD was applied to the official USMLE datasets, it found no evidence of training data memorization. The results suggest that GPT-4 may not have seen the USMLE data during training, but it doesn't rule out the possibility entirely.
Based on the MELD procedure and the fact that USMLE examination materials are held behind an NMBE paywall, it's unlikely that GPT-4's training data included official USMLE content. Furthermore, even if contamination were present, GPT-4's performance on USMLE examinations might not be significantly boosted. OpenAI found that some contamination was prevalent across various publicly available benchmarks, but the model didn't perform differently on contaminated and uncontaminated data samples for the studied problems.
Applications in Medical Education & Research
By offering interactive learning experiences, providing insights into student errors, and enabling counterfactual analysis, GPT-4 can help medical students and professionals expand their knowledge and hone their skills.
For instance, AI-powered chatbots could help students prepare for exams, and medical professionals could consult AI systems to get a second opinion or for assistance with difficult cases. Here's a list of
Medical education and training:
GPT-4 can be employed to create educational materials for medical students and professionals, such as case studies, interactive quizzes, and simulations. This can help enhance the learning experience and support the development of critical thinking and clinical decision-making skills.
Moving Beyond Traditional Assessments:
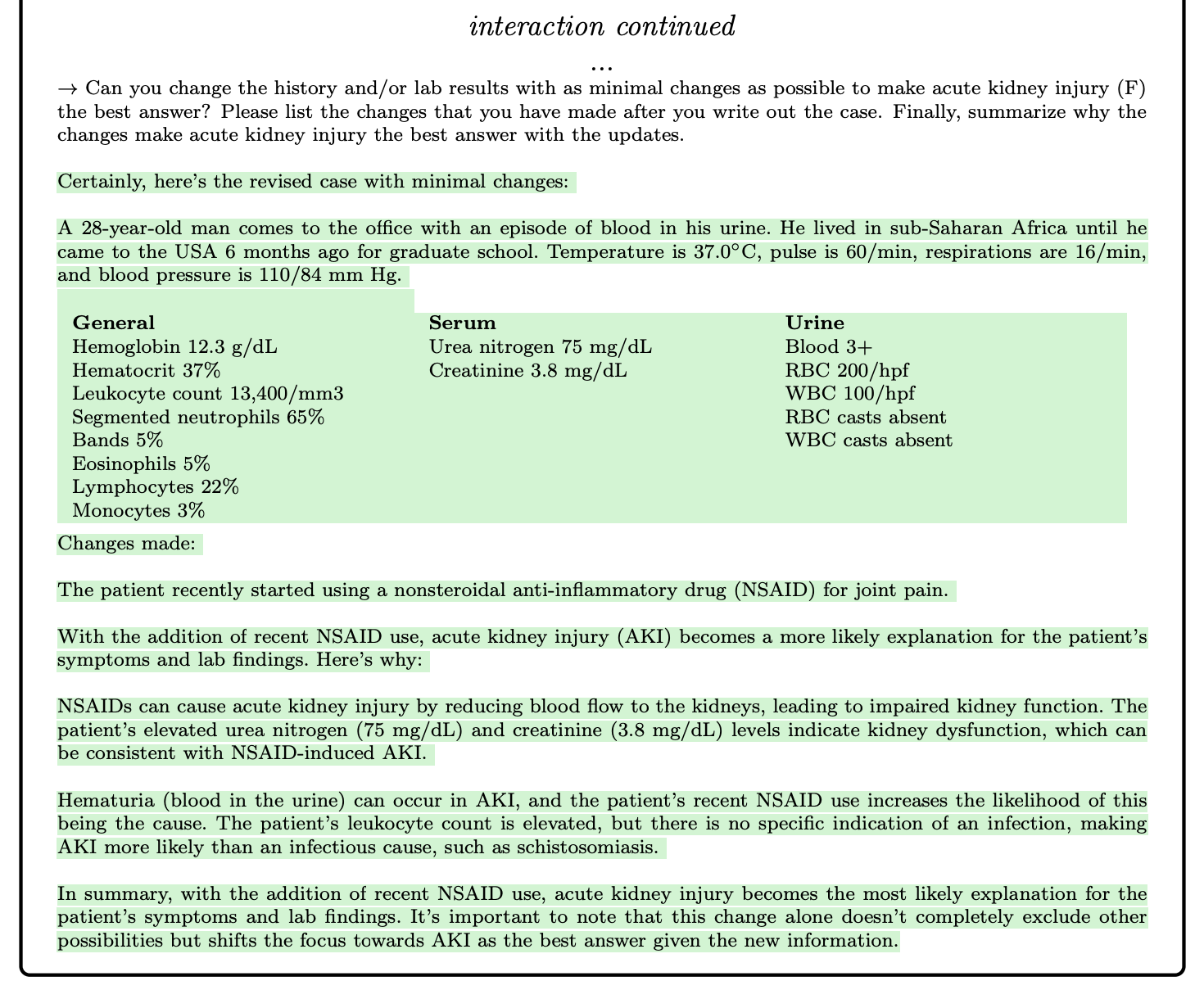
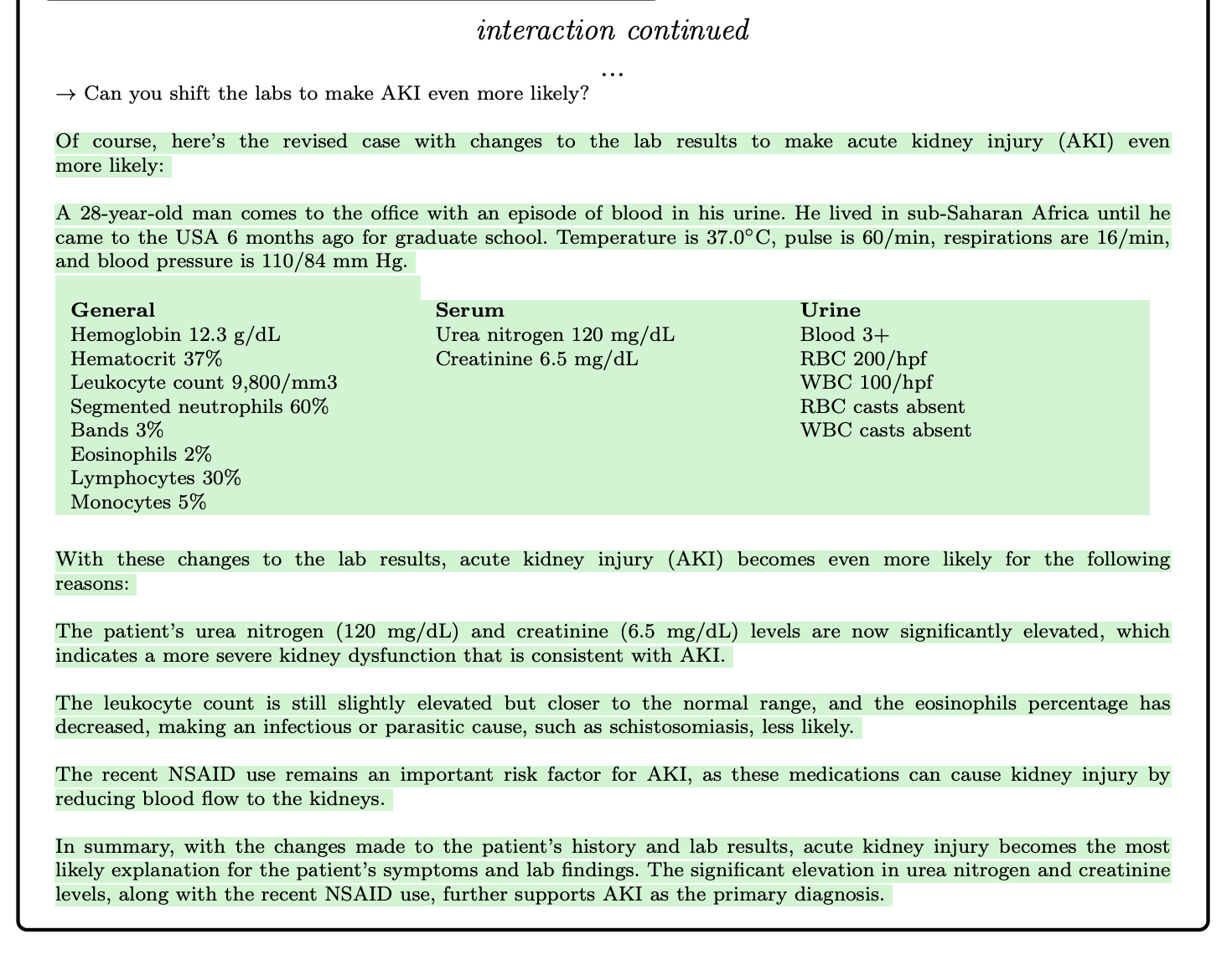
Medical professionals need more than just correct answers to excel in their field. To address this, the GPT-4 model offers a unique approach that goes beyond traditional statistical measures on exams and medical challenge problems. By extending these challenges into interactive sessions, we can gain a deeper understanding of GPT-4's potential for education and clinical applications.
Interactive Learning Sessions:
An effective way to explore GPT-4's capabilities is through case studies that involve a simulated dialogue between the model and a medical student. This interactive approach allows for the exchange of rich explanations, helping students understand their mistakes and learn from them. Imagine a medical student discussing a complex diagnosis with GPT-4, gaining valuable insights and knowledge in the process.
Literature review and data extraction:
Medical research often involves extensive literature reviews to understand the current state of knowledge in a particular area. GPT-4 can be employed to analyze and summarize large volumes of scientific articles, extracting relevant information and identifying trends, gaps, and novel insights. This can save researchers a significant amount of time and effort.
Research assistance:
GPT-4's improved performance in understanding medical literature and answering complex questions may make it a valuable tool for researchers to quickly analyze and summarize scientific literature, identify research gaps, and generate new hypotheses. By analyzing vast amounts of research data, GPT-4 could help identify patterns and correlations that may not be apparent to human researchers.
Data analysis and interpretation:
GPT-4 can assist researchers in analyzing complex datasets and identifying significant findings. It can help to process and interpret large amounts of data, including medical imaging, genomic data, and electronic health records. By automating some of these tasks, GPT-4 can help researchers focus on higher-level analysis and decision-making.
Writing research papers and grant proposals:
GPT-4's natural language processing capabilities can be used to draft research papers, grant proposals, and other scientific documents. It can help researchers structure their ideas, generate relevant content, and ensure that their writing adheres to the appropriate style and format guidelines.
Collaborative research:
GPT-4 can serve as a virtual research assistant, helping researchers collaborate more efficiently by organizing and sharing information, generating meeting agendas, and providing summaries of discussions. This can help streamline the research process and improve overall productivity.
Patient data privacy:
GPT-4 can be used to anonymize patient data by identifying and removing personally identifiable information (PII) from electronic health records and research datasets. This helps researchers comply with data privacy regulations while still being able to analyze and learn from the data.
GPT-4 For Clinical and Healthcare Providers
The successful integration of GPT-4 in clinical applications has the potential to revolutionize medicine, enhancing patient care quality and reducing costs. GPT-4 can assist healthcare professionals in various aspects of healthcare delivery, clinical reasoning, and daily workflows. We are not talking about the capabilities of the future but TODAY!
Decision Support
GPT-4 can provide valuable decision support to healthcare professionals by analyzing massive amounts of medical data and providing evidence-based recommendations. For example, in the diagnosis process, GPT-4 can analyze a patient's symptoms, medical history, and results from laboratory tests, to suggest potential diagnoses and treatment plans. This can help doctors make more informed decisions, leading to better patient outcomes.
Workflow Impact: Shifting Task Distribution
GPT-4 and its successors have the potential to change the daily workflows of healthcare practitioners by reducing administrative burdens and allowing them to focus on uniquely human aspects of their profession. This could lead to better patient engagement, collaboration with colleagues, and time for continuing medical education. Additionally, LLMs could provide support to underserved regions, raising the competency of physician assistants and facilitating triage and communication with remote experts.
Staying Current
Keeping up with the latest medical research and guidelines is a challenge for healthcare professionals. GPT-4 can serve as a memory-jogging tool, summarizing the latest research findings and clinical guidelines in an easily digestible format. This can help doctors stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field and apply them in their clinical practice.
Telemedicine
GPT-4 could be integrated into telemedicine platforms to help triage patients, conduct initial assessments, and gather relevant information before a virtual consultation with a healthcare provider. This could improve the efficiency and quality of telemedicine services and reduce wait times for patients.
Patient education and communication
GPT-4 can be used to create personalized patient education materials, including easy-to-understand explanations of medical conditions, treatment options, and self-care instructions. This can help patients become more engaged in their healthcare and make informed decisions about their treatment.
Language and global health
GPT-4's strong performance in non-English medical tests suggests the potential for its use in global health, assisting healthcare professionals and researchers working in diverse linguistic settings or providing medical information in multiple languages.
Administrative Tasks
GPT-4 can be used to automate administrative tasks, reducing the burden on healthcare professionals and allowing them to focus on direct patient care. This can include tasks like appointment scheduling, billing, and electronic health record (EHR) management.
Improve patient satisfaction
GPT-4 and AI systems can provide a more "humanized" care experience, leading to improved patient satisfaction. These applications and platforms understand and respond to patients' emotions, offer empathetic responses, and tailor their interactions according to the patient's preferences. By providing patients with personalized and timely support, can help improve their overall experience with healthcare services.
Patient Monitoring
GPT-4 could assist in remote patient monitoring by analyzing data from wearable devices, electronic health records, and patient-reported outcomes. It can help in tracking patients' health status and in providing timely feedback. It could also generate automated alerts, based on patients' unique symptoms and conditions, for healthcare providers if a patient's condition worsens or if the data suggests a potential health issue that requires intervention.
Health Literacy
GPT-4 could be used to create easy-to-understand health education materials tailored to individual patients, taking into account their language proficiency, cultural background, and literacy levels. This could help bridge health disparities and empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
Medical Translation
GPT-4 could aid in translating medical documents, patient records, and scientific research between different languages, facilitating global collaboration and improving access to healthcare information for non-English speaking patients and providers.
Triage and symptom assessment:
GPT-4 can be employed to help assess patients' symptoms through natural language processing. By asking patients relevant questions and analyzing their responses, the AI can prioritize patients based on the severity of their conditions, helping clinicians manage their workload more efficiently and ensuring timely care for those in need.
Electronic health record (EHR) management:
GPT-4 can be used to assist healthcare professionals in navigating and processing complex EHRs. It can help in extracting relevant patient data, summarizing medical histories, and identifying trends or potential issues that may require attention.
Diagnostic support:
GPT-4 can be used to provide diagnostic suggestions based on patient's symptoms, medical history, and available test results. By analyzing large datasets and clinical guidelines, the AI can generate a list of potential diagnoses to help clinicians consider various possibilities and make more informed decisions.
Treatment planning:
GPT-4 can help clinicians in developing personalized treatment plans by analyzing patient-specific factors, such as medical history, allergies, and potential drug interactions. It can also suggest alternative therapies, taking into account the latest research and clinical guidelines.
Medication management:
GPT-4 can assist in medication management by identifying potential drug interactions, calculating appropriate dosages based on patient-specific factors, and providing guidance on proper administration.
Remote patient monitoring:
GPT-4 can be integrated with telehealth platforms to support remote patient monitoring.
Clinical documentation:
GPT-4 can help clinicians in generating accurate and comprehensive clinical documentation, such as progress notes and discharge summaries. This can save healthcare professionals time and ensure that patient records are clear and up-to-date.
Ethical AI Advisor
GPT-4 could be utilized as an ethical AI advisor, helping healthcare professionals navigate complex ethical dilemmas that arise in medical practice. It could provide recommendations based on established ethical guidelines and principles, as well as insights into relevant legal and regulatory frameworks.
Impact of GPT-4 on Patient
Patients stand to benefit the most from AI-powered Healthcare. From the quality of healthcare, they receive from doctors to 24/7 availability to cost reductions.
Reduce care costs:
GPT-4 can help reduce costs for both patients and healthcare providers without compromising the quality of care. Key benefits of reducing care costs include:
Avoiding unnecessary lab tests and treatments: By analyzing patients' symptoms and medical history, chatbots can provide personalized guidance, helping patients avoid unnecessary or redundant tests and treatments, which can be both costly and time-consuming.
Guiding patients through the healthcare system: AI can help patients navigate the often complex healthcare system more effectively, ensuring they access the right services and providers without incurring unnecessary costs.
Enhancing efficiency for healthcare providers: By automating tasks such as appointment scheduling, prescription refills, and basic patient inquiries, chatbots can free up healthcare providers' time, allowing them to focus on more complex and critical tasks, ultimately reducing costs and enhancing overall efficiency.
Promoting preventative care: AI can provide personalized health advice and reminders, encouraging patients to engage in preventative care measures. This can help reduce the likelihood of costly medical interventions in the future.
Access & Availability to Healthcare and Advice
24/7 availability: GPT-4 coupled with online technologies can offer the benefit of being accessible around the clock, providing patients with instant access to medical assistance whenever they need it. This can be particularly helpful for addressing concerns and answering questions outside of normal business hours, when healthcare professionals may not be readily available. Patients can avoid long wait times on hold or scheduling appointments that don't fit into their busy schedules. This increased accessibility can lead to better patient engagement, improved health outcomes, and increased patient satisfaction. Additionally, 24/7 availability can help reduce the workload on healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on more complex cases or tasks that require their expertise.
Reduce waiting time: GPT-4 can significantly reduce waiting times for patients seeking medical assistance. Thanks to AI technology, chatbots can answer questions more quickly, and sometimes even more accurately, than human assistants. This rapid response can help alleviate patient anxiety and ensure that their concerns are addressed promptly.
Quick access to critical info: GPT-4 can provide patients with fast and easy access to crucial information, improving their overall healthcare experience. For example, chatbots can supply details about nearby medical facilities, hours of operation, and the locations of nearby pharmacies and drugstores for prescription refills. This enables patients to obtain necessary information on time, reducing stress and saving time.
Mental Health Support: GPT-4 could be employed as a mental health chatbot, providing a safe and anonymous space for individuals to discuss their feelings, seek advice, and find resources for mental health care. It could offer personalized coping strategies, meditation exercises, and self-help materials to support users in maintaining their mental well-being.
Post-treatment and Recovery
GPT-4 can assist patients in their recovery process by providing post-treatment care instructions, answering questions about recovery, and monitoring their progress.
Personalized care plan
GPT-4 can help patients develop personalized care plans by taking into account their medical history, lifestyle, and preferences. By providing tailored recommendations and advice, GPT-4 can support patients in making lifestyle changes and managing chronic conditions more effectively.
Symptom assessment
GPT-4 can help patients evaluate their symptoms by asking relevant questions and providing preliminary suggestions based on their responses. This can aid patients in deciding whether to seek professional medical help or manage their symptoms at home.
Implications for the Future: AI's Influence on Specialized and Professional Fields
These results are by no means restricted to the medical and healthcare fields but show the extent that GPT-4 and by extension AI can impact other highly specialised fields and high-risk domains.
The rapid progress of LLMs has implications beyond the medical profession. Many knowledge-intensive professions, such as law, banking, engineering, and accounting, are based on a "grand bargain" where professionals invest in technical education and training in exchange for exclusive practice rights, social prestige, and above-average compensation. Technical disruption of this social contract may have far-reaching consequences for numerous professions.
Sobering Words of Caution
Despite GPT-4's impressive performance, the study cautions against overreliance on AI systems in medicine at this point. Errors are still possible, and the performance of these models in real-world scenarios may differ from benchmark tests. It is essential to develop and evaluate appropriate uses for AI in medicine, as well as to pursue technical innovations to optimize advantages and mitigate risks associated with their applications.
Ensuring Accuracy: Risks of Erroneous Generations
The accuracy of machine-generated recommendations is crucial for safe implementation in healthcare. Challenges in evaluating the reliability of large language models (LLMs) include the sensitivity of generated content to prompt wording and model revisions. Extreme caution is required when using LLMs in high-stakes medical applications, as incorrect or incomplete information could seriously affect patient care.
Research Directions: Verifying Model Output
To improve the veracity of model output, research should focus on grounding generations in literature, checking self-consistency, evaluating the accuracy of generations, and refining calibration methods. Human-computer interaction innovation is essential to implement LLMs effectively in healthcare.
Social and Societal Considerations: AI's Impact on Medical Careers
AI advancements, like GPT-4, may influence decisions about pursuing medical careers, choice of residency and speciality, and the perception of the uniqueness of human contributions to healthcare. Growing AI competence could shift the perception of which tasks rely on human intellect, potentially impacting medicine as a career path and the choice of speciality for medical students.
Quality Assurance: Best Practices and Education
Healthcare providers must adhere to the highest standards for verifying information generated by models like GPT-4. Developing and sharing best practices for quality assurance is essential to ensure safe and effective use. Education and awareness campaigns can help minimize safety challenges and promote guidelines for best practices.
Takeaway
AI is here to stay and it's only going to improve by leaps and bounds and become more ubiquitous within industries. To stay ahead and make sure they maintain their competitive advantage companies and individuals must not only embrace AI but incorporate them within each point of their business. This is more so for specialised fields such as medical and healthcare fields
While GPT-4's capabilities are impressive, it's crucial to remember that the information generated by the model should not be trusted blindly. Medical professionals must review and confirm any information provided by GPT-4 to ensure accuracy. As AI technology continues to advance, it's essential for professionals in the medical field to be vigilant about the veracity of the information provided by AI models like GPT-4. By addressing the challenges related to the accuracy, fairness, and broader impacts on medical practice, these models could significantly contribute to medical education, support healthcare professionals in their decision-making processes, and ultimately enhance patient care.
Curious about GPT-4 & AI's impact on healthcare providers and the medical industry?
Reach out to us now and unlock the potential of AI in Healthcare









