Prompting
Previously, we ventured into the world of AI Prompts, unveiling a captivating prompt structure and hinting at an intriguing process. In this lesson, we'll delve deeper into the stimulating prompting process, exploring each enthralling section with keen attention. Join us as we illuminate the intricacies of this essential aspect of AI prompt engineering.
Get ready to embark on a captivating journey through the world of AI Prompting! This lesson offers a comprehensive and systematic approach to help you skillfully craft AI prompts for any purpose. The framework provided will be your go-to guide for understanding, testing, customizing, and documenting every prompt you encounter.
By deconstructing the prompting activity into components, you'll unlock the ability to experiment with diverse ways and permutations to present information within prompts for various AI models. This approach ensures you'll achieve the most exceptional outcomes for your AI endeavours.
Demystifying Prompting
At the heart of prompt engineering lies Prompting - the fascinating blend of art and science that involves designing and crafting text-based prompts in natural language for AI systems. This critical element bridges the human-AI relationship, enabling seamless and intuitive interactions with technology.
A Foolproof, Step-by-Step Framework for Prompting Mastery
While the AI landscape is ever-evolving, embracing a structured process empowers you to generate consistent, high-quality results. As you diligently apply this framework to each prompt you create, you'll evolve into a more effective and efficient prompt engineer. The icing on the cake? A clear and repeatable process minimizes trial and error, freeing up precious time and resources for other aspects of your work.
Moreover, adhering to a process guarantees that your prompts consistently meet the quality standards and guidelines you've established. Ultimately, a well-defined process fuels better results, increased productivity, and success in the dynamic field of prompt engineering.
A Glimpse into the Captivating Prompting Process
The prompting journey commences with defining your desired outcome, be it generating specific text or answering a particular type of question. Next, you'll design a prompt that propels the model towards this outcome, employing targeted keywords or phrases, providing context, or phrasing a question in a unique way.
With the prompt crafted, you'll dive into optimization through experimentation and iteration. By testing various prompt variations, gathering human evaluator feedback, and scrutinizing the model's output, you'll pinpoint the optimal prompt that delivers peak performance.
The significance of prompt engineering is immense. By fine-tuning prompts, we can elevate large language models' performance, making them invaluable for tasks such as generating high-quality text, answering questions, and even creating fresh content. In essence, prompt engineering is a pivotal factor in developing cutting-edge NLP systems and shaping AI's future.
Prompting Langauge Considerations
The best type and manner of language to construct AI prompts is clear, concise, and specific. To create effective prompts, consider the following guidelines:
- Use plain language: Avoid jargon and complicated terms. Make your instructions easy to understand so the AI can quickly grasp your intent.
- Be specific: Clearly state your expectations and desired outcomes. Provide detailed information to help the AI generate accurate and relevant outputs.
- Maintain a logical structure: Organize your prompt in a coherent manner, so the AI can easily follow your instructions and provide the desired response.
- Include examples: If possible, provide examples to illustrate the type of output you're looking for. This can help the AI better understand your expectations and generate more accurate results.
- Consider the context: Tailor your prompt to the AI system and its capabilities. Be mindful of the platform or model you're working with, and ensure your instructions are compatible with its limitations and strengths.
Language considerations: This is a big debate, but from our experience and the studies we have seen, using simple, concise English seems to be the best approach (as of the date of publishing). This may change in the future, but since LLMs are primarily built on English, it makes sense to use English. However, the latest generations of LLMs seem to be great at other major languages as well. As the field develops, we will advise professionals as necessary.
By adhering to these guidelines, you'll be able to construct AI prompts that effectively communicate your intentions and yield the desired outcomes.
An Overview of the AI Prompting Process
AI Prompts comprise 5 primary components: Task, Instructions, Context, Parameters, and Input. Depending on the use case, not all components may be required. For instance, a simple AI prompt may only include the Task component.
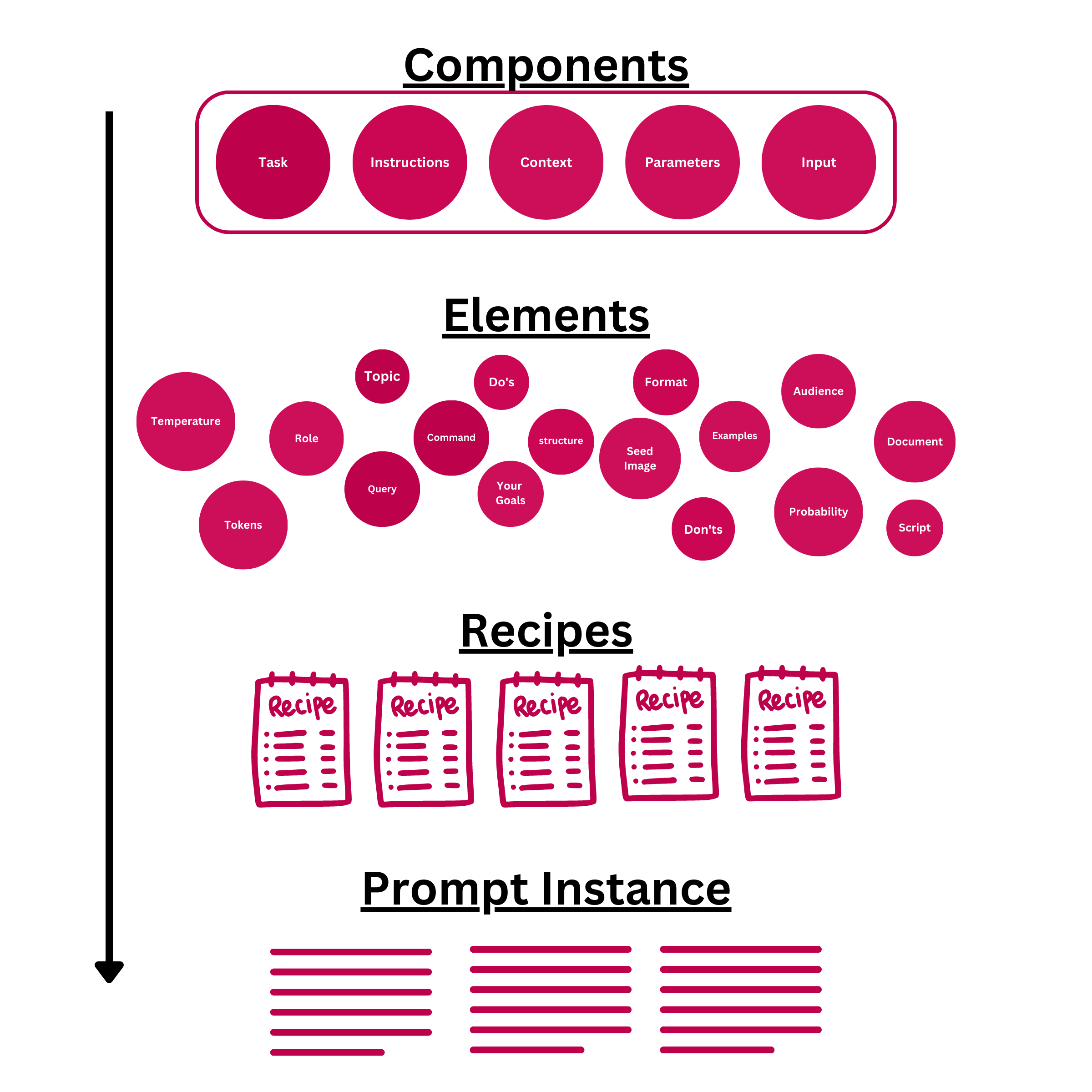
These components remain relatively fixed and are not advised to be altered. Nevertheless, each component consists of various elements, such as the Task being composed of role, command, and topic. These elements can be adjusted, rearranged, and tailored to create distinct prompt "recipes."
Elements and recipes allow for the application of one's skill and creativity. While these lessons offer standard elements appropriate for most scenarios, individuals are encouraged to infuse their personal touch. As one learns prompt engineering, adhering to the provided examples is recommended until greater proficiency is achieved.
The process entails decomposing tasks into components and elements, subsequently crafting an assortment of recipes to assess with the AI, and ultimately determining the optimal fit for the project. These recipes should be stored in one's prompt library for future utilization.
These recipes can be converted into actual prompts to be fed to the AI. For prompt engineers, this method serves as one of the most efficient ways to conceptualize, generate, and maintain prompts within one's prompt library.
A Prompt Example
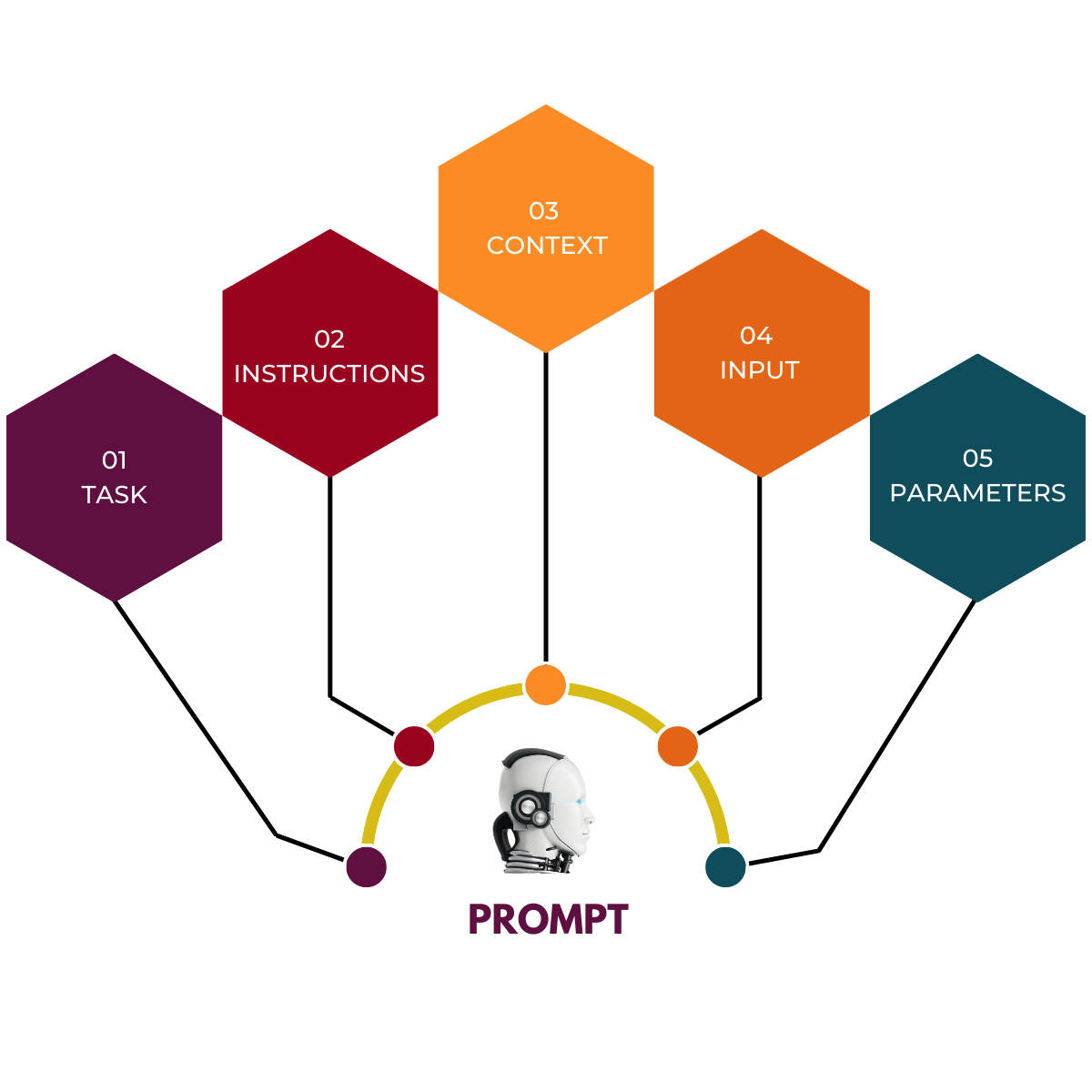
Let's ignite our exploration by examining a sample prompt and uncovering its diverse components. We've crafted this recipe and example with ChatGPT 3.5/GPT-4 in mind, but fear not—flexibility is at your fingertips! You can effortlessly adapt the prompt or structure to cater to your unique requirements.
Remember, your prompt needn't encompass all these elements and components; it's all about tailoring your approach to the system you're utilizing and the outcomes you desire. Study the table below, and join us as we unravel each facet of the prompt in the subsequent sections.
Statement of Purpose: I want to be more helpful to my subordinates at work and help them grow. One of the issues I have identified that some suffer with is imposter syndrome. I want to offer some helpful advice.
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 1 - Statement of Purpose
Before you start crafting your AI prompt, it's essential to briefly consider your goals, purpose, and desired outcome. This first step will help guide the subsequent steps in the process.
You may have some ideal examples of the output you'd like. Collect and keep these at hand.
Don't overthink it - this statement doesn't need to be complicated, as refinement will occur throughout the following steps.
From our example above we can see our statement is simple and not too complex, expressed in everyday terms and language:
Statement of Purpose: I want to be more helpful to my subordinates at work and help them grow. One of the issues I have identified that some suffer with is imposter syndrome. I want to offer some helpful advice.
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 2 - Define the Task
As you begin the process, it's essential to clearly define the task and its components. This foundational step is crucial for the success of your work.
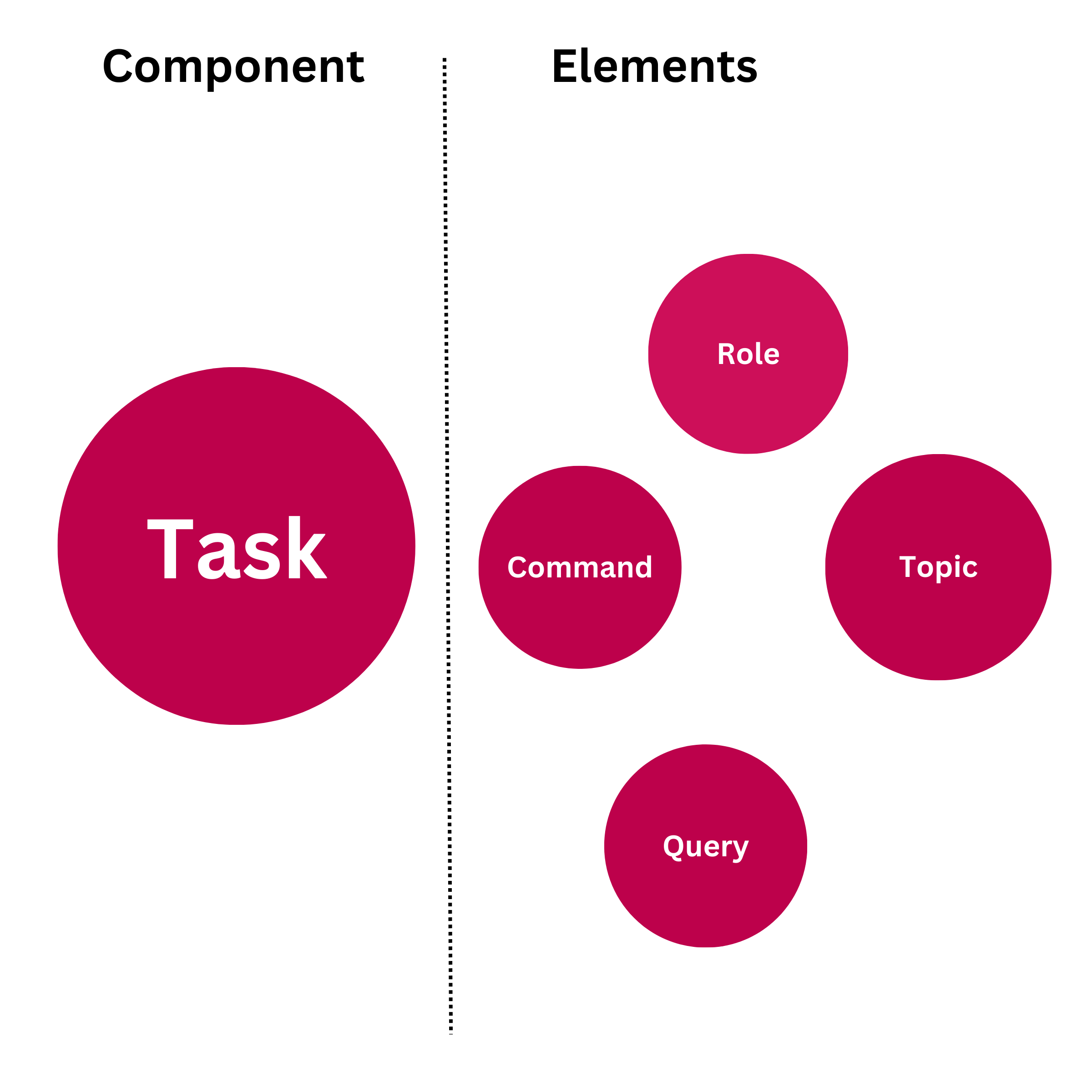
Think about the specific goals you want the AI system to achieve and the input data it will use. The task consists of several elements, such as Command or Query, the topic or subject, and the role or persona. For most modern LLMs, consider the role you want the AI to play for optimal results.
Remember to be precise. Use clear verbs and words as if you were instructing a person. For instance, instead of saying "Generate a blog post on skipping rope," say "Write a blog post on how to skip rope."
By clearly defining the task, the AI system will understand its exact purpose and what information to search for. Nail this step, and you're on the path to successful AI prompt engineering.
Again referencing our example, for the task we defined as best as possible, in simple and concise language, the Task, which is composed of the role you want the AI to take, the actual command to execute and the general or specific topic you want to write on:
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 3 - Give the AI the Right Instructions
Define the ideal output: Be specific about the desired outcome from the AI system. Clearly outline the format and characteristics of the output to give the AI a proper understanding of your expectations.
Output Format and Structure: Think about the final use case and audience. Define the length, content type, and format of the final product. For instance, "The article should be 2500 words, with each idea clearly stated in headers and a logical flow."
Output Characteristics: Define the tone, style, and level of detail, such as "The article should be written in a friendly, inspiring, conversational tone using natural language."
Outline the points and topics you want to be included: Provide the AI system with the information and topics necessary for the output. Specify any specific ideas or perspectives you'd like the AI to include.
"Do's and Don'ts": Set boundaries for the AI. Offer guidelines and restrictions to ensure the output aligns with your expectations and avoids unwanted or problematic content.
Ideal Input and Output Examples: Provide clear examples of the desired input and output. This helps the AI system understand the tone, style, and format you want for the output.
Incorporate "Ideal Input and Output Examples" in your AI prompt engineering plan to ensure the AI system delivers relevant, high-quality, and tailored content that meets the specific needs and expectations of your target audience and use case.
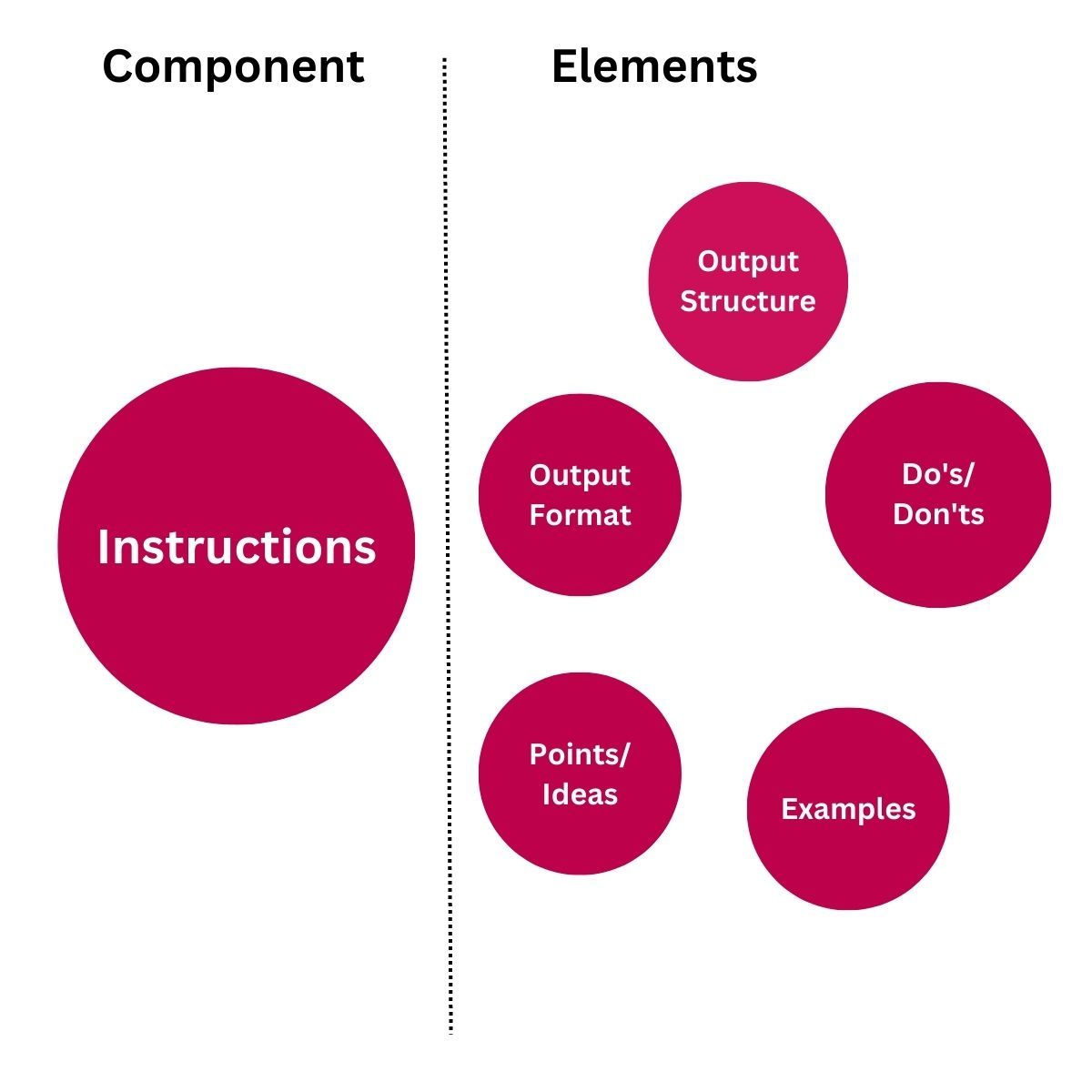
In our example, we've identified the following elements for the instruction component:
- Output structure and format
- Qualities of the output
- Content
- Do's and Dont's
We've made sure to keep the language simple and concise to the best of our ability.
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 4 - Context: Additional Guidance for the AI
As a prompt engineer, you can enhance AI output by providing extra guidance. This goes beyond basic instructions and offers a deeper understanding of your unique requirements. By doing this, you ensure that the AI output is relevant, high-quality, and tailored to your needs.
Desired Point of View or Perspective: Specifying the desired point of view is crucial for aligning the AI output with your vision. Think about your audience and the perspective that makes the most sense. Providing this context helps the AI create output that resonates with your audience.
Target Audience: Define your target audience before starting. Consider demographics like age, gender, location, interests, and values. This context helps the AI create output specifically for your audience. Don't forget about your audience's brand archetype, which guides the AI in creating output consistent with your audience's expectations.
Purpose and Use Case: Defining the purpose and use case sets the direction and provides a roadmap for the AI. Specify the context in which the output will be used to ensure it meets specific requirements. This step is critical for producing output that's relevant, high-quality, and tailored to your needs.
Supplementary Information and Data: Providing additional data and background information empowers the AI to create a unique, relevant, and high-quality output. More data also leads to greater accuracy, ensuring the output meets your specific needs and expectations.
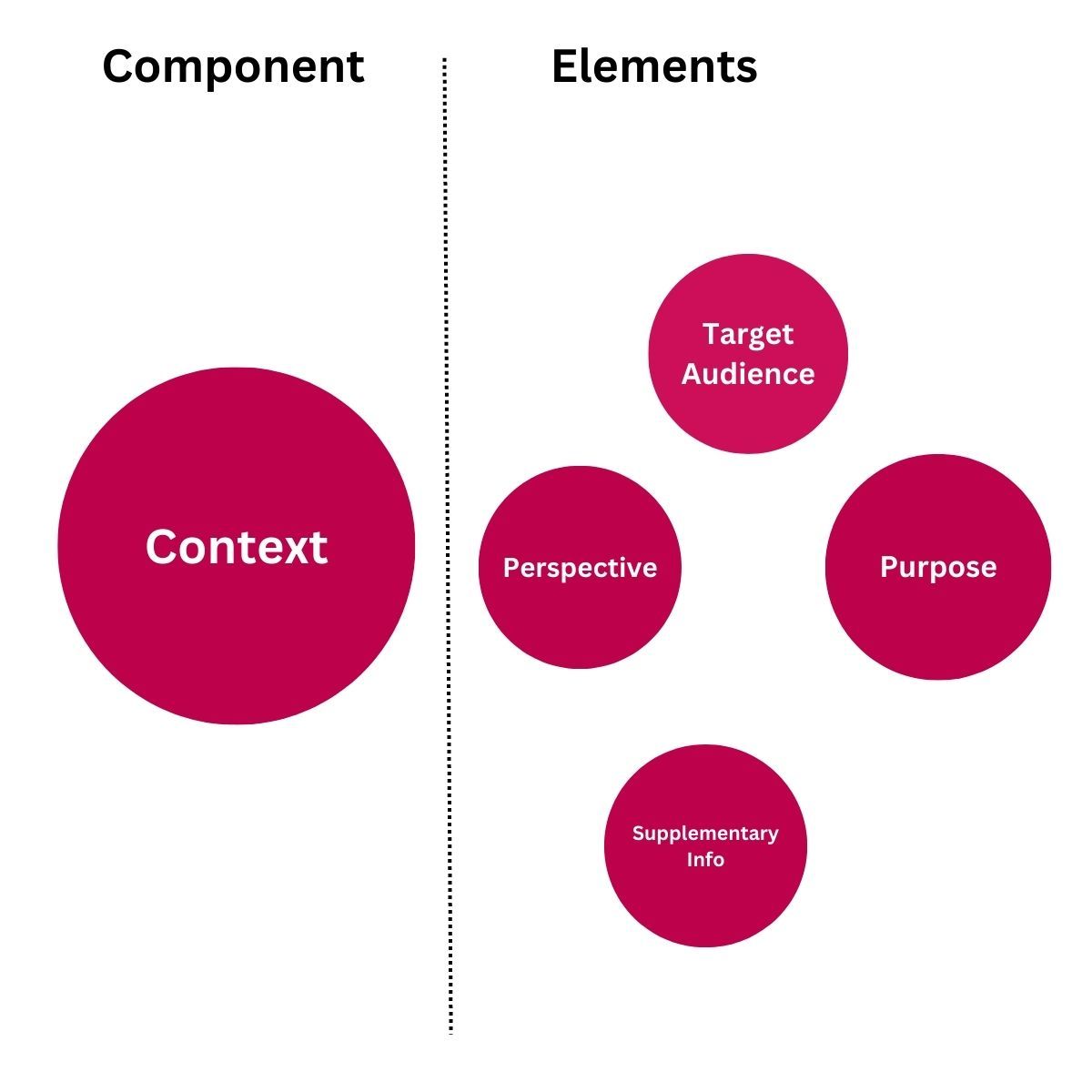
In our example, we've outlined the following elements for the context component:
- Perspective
- Your goal
- Target Audience
We've ensured that the language remains simple and concise for optimal clarity.
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 5 - Parameters: Setting Expectations for AI
In AI prompt engineering, specifying the parameters of your model or platform is essential. It helps set clear expectations for the AI system, ensuring it understands the desired complexity, data processing, and output format.
For a machine learning model, specify the accuracy, confidence level, data processing, and computational resources. If you're using a platform, define the desired output format and specific features or functionality. For example, in a natural language generation platform, set the level of detail and complexity for the output. Some of these settings control how deterministic the model is when generating output. Generally, you want to keep these settings low if you are looking for exact answers and higher if you are looking for the model to be more creative.
In summary, the "Parameters" step allows you to dictate requirements and limitations for your AI system. Providing this information ensures your AI operates effectively and efficiently, producing the desired output in the correct format.
In our example, no parameters are specified since ChatGPT doesn't utilize them directly (at the time of writing). However, we'll explore additional examples in subsequent lessons, with other LLMs that may require parameter adjustments or fine-tuning.
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 6 - User Input: Transforming Existing Content
User Input refers to the text or information you want to transform. While creating content from scratch may not require this, it's useful when refining existing content, such as an email draft to your supervisor. Providing the draft as input to the AI helps improve your email, resulting in a polished and professional message with a friendly tone.
Keep in mind, user input is not a necessary part of the prompt, as it's only required when refining or working on pre-existing text or content.
In our example, we didn't specify any input because we aimed to generate content using ChatGPT's extensive knowledge.
Developing AI Prompts for LLMs: Step 7 - Output Review and Commit
The final step in the Prompting Process is executing the prompt and reviewing the output. Compare the output to your initial expectations or examples of your ideal result. You may want to tweak your prompt recipe or copy the output to a word processor for further edits before sending it off.
At this point, you have three options:
- Refine the prompt: Work on the prompt until it meets your needs. You can either refine the original prompt or use additional prompts to improve the output (known as prompt chaining). For example, if you want words and headings highlighted but didn't include that in the original prompt, you can create a new prompt to achieve the desired outcome and incorporate it into the original prompt.
- Commit to Prompt Library: When you have a successful prompt recipe, add it to your prompt library with appropriate descriptions and any other relevant information.
- Human Review and Publish: Always review the output of an LLM, as there may be inconsistencies. Use tools like Grammarly to check spelling and grammar, and have someone else review the content if possible. Once completed, publish the content, whether it's an email, presentation, or article.
Remember, there's a point of diminishing returns where spending more time on a prompt may not yield the exact result you had in mind. It's essential to find the right balance between prompt refinement and moving forward with the output.
Summary & Conclusion: Mastering AI Prompt Engineering
The AI Prompting process is a crucial aspect of prompt engineering, involving designing and crafting text-based prompts for AI systems. By following a structured framework, you can effectively create and optimize AI prompts for various purposes. This includes defining the task, providing clear instructions, adding context, specifying parameters, and incorporating user input when necessary.
Breaking down the prompting activity into components enables testing different permutations, ensuring the best outcome for your AI model. This comprehensive approach improves large language model performance and contributes to the development of advanced NLP systems and the future of AI.
With a solid grasp of prompt structure and process, you're ready for the next exciting lesson: