The rapid growth and integration of artificial intelligence in various industries is fundamentally reshaping the global job market, leading to the emergence of new professions, skills, and challenges.
New AI technologies like ChatGPT are rapidly changing the job market, leading to the creation of a range of new AI-focused roles and job titles.
As companies race to leverage cutting-edge AI, there has been a surge in demand for talent that can build, manage, and apply these powerful new tools.
The Proliferation of AI Job Postings
In recent months, job postings mentioning AI technologies like GPT and ChatGPT have absolutely exploded. According to LinkedIn data, such postings have increased 21x since ChatGPT's launch in November 2022. Other sites like Indeed have seen similar spikes, with AI-related job postings reaching all-time highs this summer.
While hiring has slowed in some sectors, demand for AI talent remains red-hot. The data makes it clear that organizations across industries want to tap into the transformative potential of AI.
The Emergence of Novel AI-Focused Roles
With this surge in demand, novel AI-centric roles are rapidly emerging. Job titles like "Chief AI Officer," "AI Engineer," "Head of AI," and "AI Data Scientist" barely existed a few years ago but are quickly becoming commonplace.
According to LinkedIn, the number of companies with a Head of AI role has nearly tripled over the last five years. As organizations integrate AI more deeply, they are creating specialized positions to build, manage, and oversee their AI capabilities and strategy.
Data from LinkedIn's Future of Work report vividly illustrates the trend. The mentions of terms like "GPT" or "ChatGPT" in job postings have seen a massive surge, growing 21 times since November 2022. This burgeoning sector now features a myriad of job titles: chief AI officer, AI engineer, head of AI, AI specialist, AI advisor, and AI data scientist, to name a few.
The Demand-Supply Dynamics in the AI Job Market
While the demand for AI skills remains robust, the supply is trying to catch up. Job platforms like Indeed and ZipRecruiter have reported record high listings for generative AI-related jobs, underscoring the growing appetite for AI talent.
The Wider Context of Hiring in the AI Domain
Despite the spike in AI job listings, the hiring pace is decelerating, suggesting a highly competitive market for AI roles. As put by Cory Stahle, the demand remains warm even if it's no longer at a rapid boil.
The Balance: Job Creation vs. Job Loss due to AI
The jury is still out on the net effect of AI on global employment. While some, like Goldman Sachs, predict massive job losses, others like the World Economic Forum, anticipate a more balanced outcome. The disparity in predictions mirrors the uncertainty when driverless cars were introduced, with many prematurely anticipating the demise of driver roles.
Growing Need for Ethical Considerations in AI
As AI becomes increasingly embedded in business systems, there's a growing emphasis on ethical considerations. Roles such as ethicists and chief trust officers are predicted to proliferate. Companies will be under greater scrutiny to ensure their AI systems are unbiased and transparent.
AI Skills: The New Gold Standard
LinkedIn data underscores a crucial trend: professionals are rapidly upskilling in the domain of AI. With a 13% increase in generative AI-related skills post-ChatGPT's launch, it's evident that the workforce is gearing up for the AI-driven future.
AI Skills that are in Demand
Skills such as natural language processing, classification, and "question answering" are not only desired but essential. These skills underscore the breadth and depth of expertise required to navigate the AI landscape successfully.
A Closer Look at The Data
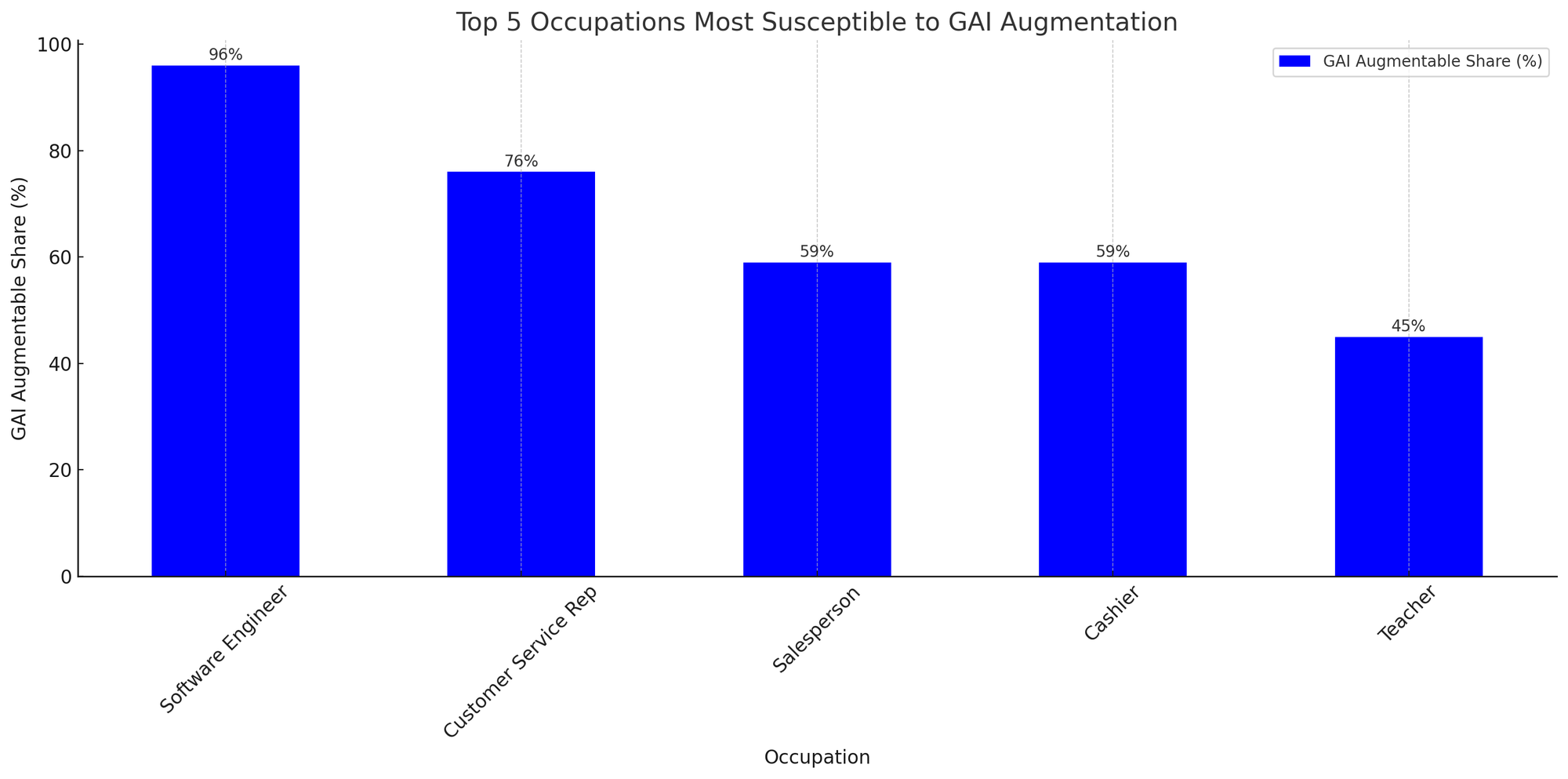
Based on the provided data, here's a quick overview of the occupations in terms of skills augmentable by GAI (Generative AI) and people-specific/specialized skills:
High Augmentation by GAI:
- Software Engineer: 96% of the skills are potentially augmentable by GAI.
- Customer Service Rep: 76% of the skills can potentially be augmented.
- Salesperson and Cashier: Both at 59%.
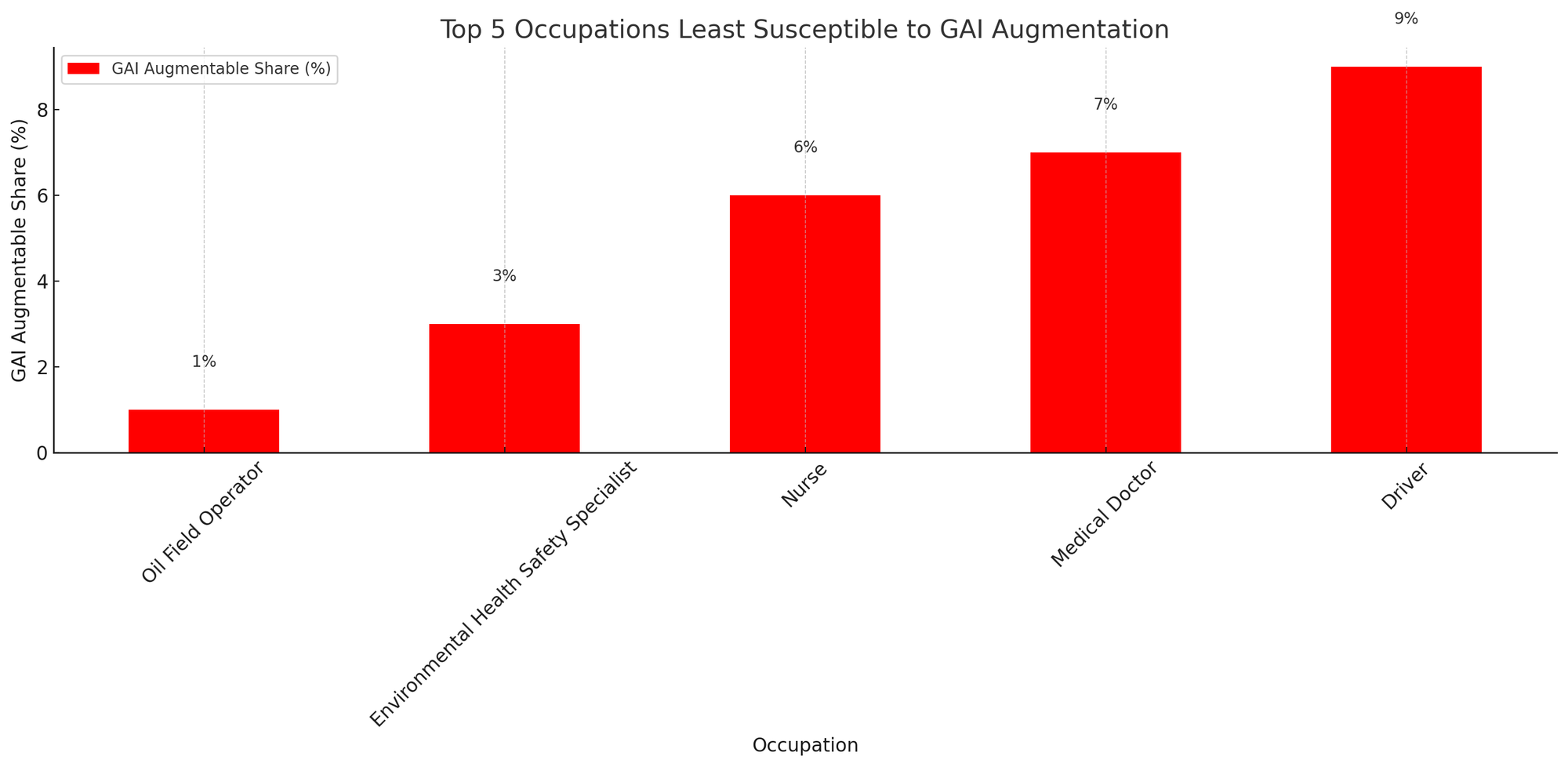
Low Augmentation by GAI:
- Oil Field Operator: Only 1% of the skills are augmentable by GAI.
- Nurse and Medical Doctor: 6% and 7% respectively, indicating that the medical field, especially roles involving direct patient care, relies heavily on specialized human skills.
- Environmental Health Safety Specialist: 3% augmentable by GAI.
High People and Specialized Skills:
- Oil Field Operator and Nurse: 89% and 90% respectively. This suggests that these roles require specialized training and a significant human touch.
- Construction Specialist: 78%, indicating the importance of hands-on skills in the construction sector.
Low People and Specialized Skills:
- Software Engineer and Customer Service Rep: Only 3% and 4% respectively, suggesting that a lot of tasks in these roles could potentially be automated or assisted by GAI.
Takeaways:
- Occupations like Software Engineering and Customer Service could see a significant shift in the nature of tasks performed by humans. As GAI takes over repetitive or analytical tasks, humans in these roles might focus more on creative, decision-making, or strategic aspects of their jobs.
- Roles like Nursing, Medical Doctors, and Oil Field Operators seem to have a strong human component that's difficult for AI to replicate or augment. These professions require hands-on expertise, intuition, and personal care, which might be challenging for AI to mimic.
- The Teaching profession is an interesting case. While GAI can assist in lesson planning or curriculum development, the human touch in delivering lessons, understanding student needs, and personal mentorship is irreplaceable.
- The balance between GAI and human skills is crucial. For instance, in jobs where GAI augmentation is high, there is a risk of job displacement. However, it's also an opportunity for professionals to upskill, learn to work alongside AI, and focus on tasks that require human intuition, creativity, and empathy.
- Training and Education: As GAI becomes more prevalent, there will be a need for widespread training and education to help workers adapt to the changing job landscape. This includes understanding how to use GAI tools and focusing on developing skills that are complementary to what GAI offers.
- Ethical Considerations: As GAI starts augmenting more skills, especially in critical areas like medicine or safety, there will be ethical dilemmas to address, such as responsibility for errors or the extent to which we can trust AI recommendations.
Conclusion:
The age of AI has ushered in a transformative period for the global job market. As AI continues its integration into every industry, professionals and businesses alike must adapt, upskill, and anticipate future shifts. Only by doing so can they harness the full potential of AI while navigating its associated challenges.